

Web 3.0
Written by
Sandeep Ozarde
Written by
Sandeep Ozarde
Web 3.0
The inventor of the World Wide Web and one of Time Magazine’s 100 Most Important People of the 20th Century, Sir Tim Berners-Lee is a scientist and academic whose visionary and innovative work has transformed almost every aspect of our lives.
Having invented the Web in 1989 while working at CERN and subsequently working to ensure it was made freely available to all, Berners-Lee is now dedicated to enhancing and protecting the web’s future. He is a Founding Director of the World Wide Web Foundation, which seeks to ensure the web serves humanity by establishing it as a global public good and a basic right.
The Semantic Web, sometimes known as Web 3.0, is an extension of the World Wide Web through standards set by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The goal of the Semantic Web is to make Internet data machine-readable.
"I have a dream for the Web [in which computers] become capable of analyzing all the data on the Web – the content, links, and transactions between people and computers. A "Semantic Web", which makes this possible, has yet to emerge, but when it does, the day-to-day mechanisms of trade, bureaucracy and our daily lives will be handled by machines talking to machines. The "intelligent agents" people have touted for ages will finally materialize."
People keep asking what Web 3.0 is. I think maybe when you’ve got an overlay of scalable vector graphics – everything rippling and folding and looking misty – on Web 2.0 and access to a semantic Web integrated across a huge space of data, you'll have access to an unbelievable data resource.
– Tim Berners-Lee, 2006
Web 3.0 is the next stage in the evolution of the Internet, and it will make the Internet smarter by processing information with human intelligence via artificial intelligence systems that can run intelligent programmes to assist users. Humans and machines will be able to connect to data more easily as a result, and artificial intelligence will play an important role in making the Web 3.0 internet smarter and more capable of processing information.
Decentralization and artificial intelligence have been added to Web 3.0, allowing computers to analyse data in the same way that humans do, providing users with valuable content tailored to their specific needs. The Web 3.0 system can be further defined as the decentralised interconnection of data, which represents a significant advance in the second generation of Internet evolution of Web 2.0. The core idea behind Web 3.0 is the evolution of a "semantic web" capable of understanding knowledge and data, with the goal of creating a smarter and more connected Internet. Web 3.0 strives to provide more personalised and relevant information at a faster rate by utilising artificial intelligence and advanced machine learning techniques. Web 3.0 is a unified web interface in which machines can comprehend and catalogue data in the same way that humans do. The most important Web 2.0 tools and technologies are Javascript, mobile computing, and the cloud. Web 3.0 is the next step in the evolution of the Internet, which may incorporate blockchain technology and decentralisation tools.
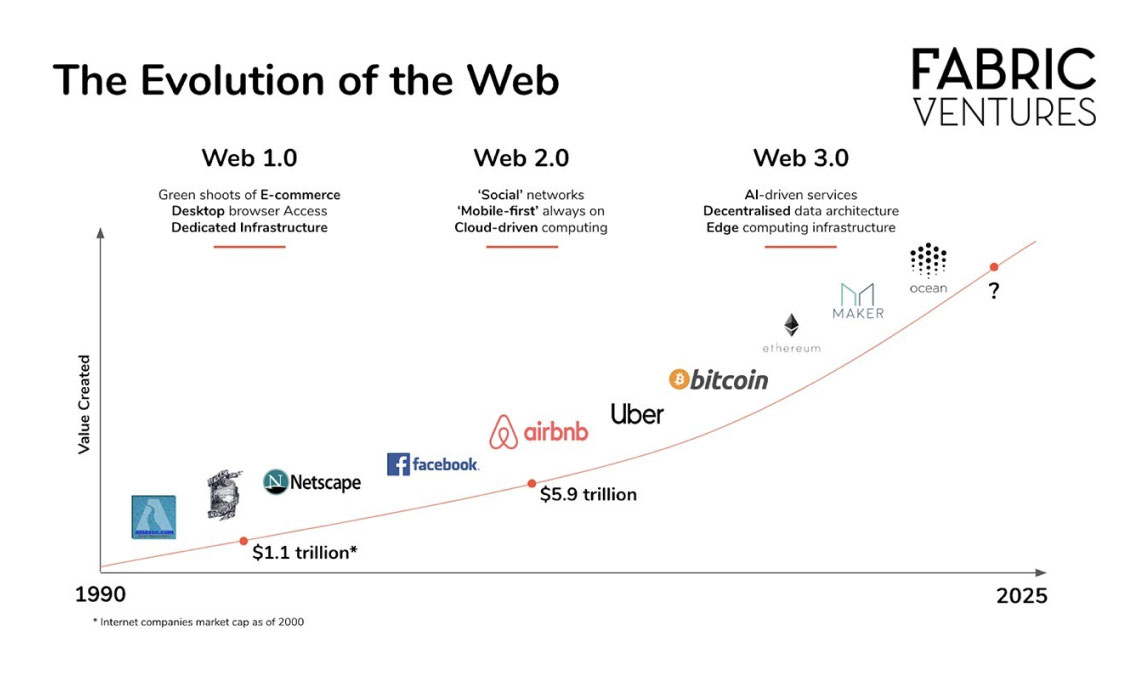
Credit: Fabric Ventures
The Web 3.0 system has the potential to revolutionise the Internet world through the use of blockchain technology. It would not be surprising if the Internet moves from Web 2.0 to Web 3.0 in the coming years as technologies evolve in tandem. As we progress toward Web 3.0 and Web 3.0 technologies, the Internet will become more scalable and exponentially more integrated into our daily lives. Web 3.0 will imply a highly distributed Internet that will supersede DLT as a blockchain in terms of changing how information is organised. Information will become more connected and ubiquitous with Web 3.0 because Internet-connected devices will no longer be limited to computers and smartphones. Data will be interconnected and decentralized, which will be a significant advancement over Web 1.0.
Web 3.0 refers to the next generation of the Internet, in which websites and applications will be able to use technologies such as machine learning (ML) to manage data intelligently and humanely, Big Data, and Decentralized Ledger Technology (DLT), among other things. Web 3.0, also known as Semantic Web (as defined by Tim Berners-Lee) Tim Berners-Lee is a part of the next generation of the Internet, which will make the Web smarter or allow it to harness the power of artificial intelligence to process information with intelligence comparable to human intelligence (artificial intelligence).
Many technologists, journalists, and industry leaders have used the term "Web 3.0" to predict a future wave of Internet innovation since the term "Web 2.0" was coined to describe the most recent developments in the World Wide Web. Web 3.0 is a broad term referring to the next stage in the evolution of the Internet, which is defined by decentralisation and user sovereignty, as well as an incredible understanding of the experience and utility that people derive from the online world.
Web 3.0 represents a paradigm shift for the Internet in the direction of decentralised, user-centric, and engaging online experiences. Its heir is a more interactive and interoperable internet in which users can interact with websites via server-side processing, online forms, and social networking. While Web 3.0 employs Semantic Web concepts and natural language processing to improve user experience, it also includes other features such as extensive use of AI and machine learning, as well as trustless/no-permission-required systems such as blockchains and peer-to-peer networks.
Web 3.0 is intuitive because it uses big data, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to analyse user data and behaviour in order to provide a personalised experience. Web 3.0 is a hybrid of old-school web tools and cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence and blockchain, as well as increased user interconnection and internet usage. Web 2.0 makes the Internet more interactive and accessible than Web 1.0 by leveraging technologies such as HTML5, CSS, AJAX, and Javascript. Web 2.0 is the most recent version of the Internet (a term that is frequently used interchangeably with "Web") that we are all familiar with, and Web 3.0 is its next stage. Web 3.0 represents the next iteration or phase of Web/Internet development, with the same disruptive potential as Web 2.0. Web 1.0 introduced a new digital content platform, Web 2.0 introduced user feedback, and Web 3.0 marked the beginning of a new era in Internet evolution: the visually dynamic Smart Web.
The difference between Web 2.0 and 3.0 is that Web 3.0 is more focused on the use of technologies like machine learning and AI to provide relevant content for each user instead of just the content other end users have provided. Web 2.0 essentially allows users to contribute and sometimes collaborate on on-site content, while Web 3.0 will most likely turn these jobs over to the semantic web and AI technologies.
The concept behind Web 3.0 is that websites will be able to interpret user data and become smarter as time goes on in order to provide better digital experiences. The goal of the internet is to make internet searching faster, easier, and more efficient, as well as to handle complex search phrases quickly. Web 3.0 will enable online content to be tailored to each user while protecting their privacy, adding new utility and value to the Internet and online interactions. Web 3.0 is the next step in the Internet’s evolution, ensuring that we can always take advantage of its benefits while avoiding its drawbacks.
Credit: Geek and Poke
The original cryptocurrency has been around for more than ten years, and the protocol itself is decentralized, although not all of its ecosystem is.
Blockchain-based blogging and social platform.
Decentralised exchange trading market.
A marketplace for buying and selling NFTs, itself built on the Ethereum blockchain.
Another decentralised social network, built on the Ethereum blockchain.
Decentralised cryptocurrency exchange.
Blockchain-based supply chain, provenance, and authenticity platform.
References